Browse our range of reports and publications including performance and financial statement audit reports, assurance review reports, information reports and annual reports.
System of Audit Quality Management
Please direct enquiries through our contact page.
Amelia Pomery, Senior Director – Professional Services Group, Australian National Audit Office, delivered a presentation virtually to the PASAI Leadership Program, on 4 April 2024. The presentation was titled System of Audit Quality Management.
Slides
The slidedeck for the presentation can be downloaded at Related documents on this page. The text of the slides is available below.
Overview of ANAO quality management standards
ASQM 1 – Australian standard on quality management
- The AUASB issued ASQM 1 which came into effect on 15 December 2022.
- The ANAO Auditing Standards incorporate the Australian equivalent Standard on Quality Management (ASQM 1), and our system of quality management was required to be designed and implemented by 15 December 2022.
- ASQM 1 replaced the previous Quality Control Standard ASQC 1.
Risk-based approach of ASQM 1
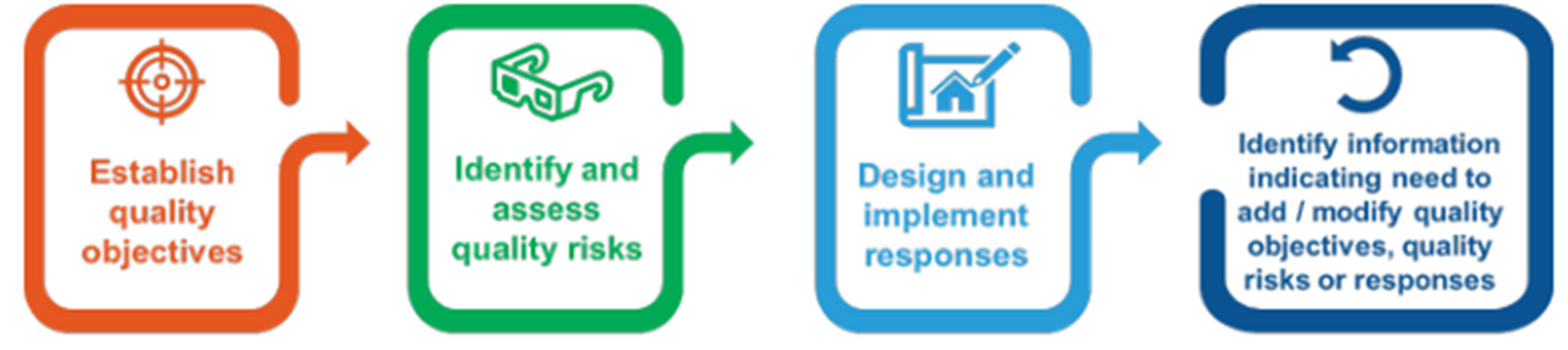
- ASQM 1 introduced a quality management approach that is focused on proactively identifying and responding to risks to quality.
- The risk-based approach is embedded in the requirements of ASQM 1 through:
- establishing quality objectives;
- identifying risks to the achievement of the objectives;
- and designing and implementing tailored responses to the quality risks.
Elements of ASQM 1

Note: acceptance and continuance are referred to as ‘audit mandate and selection’ at ANAO because we are mandated to conduct financial statements audits of all Commonwealth entities and companies, and their subsidiaries.
The new elements from ISQC 1 are:
- the risk assessment process – to implement the risk-based approach;
- information and communication (including external communication regarding the system of quality management).
ISQM 1 expanded the existing components from ASQC 1:
- Governance and leadership (formally Leadership responsibilities – expanded to include governance);
- Resources (formally Human Resources in ASCQ 1 – expanded to include technological resources, intellectual resources and use of service providers);
- Monitoring and remediation process (formally Monitoring – expanded to include root cause analysis).
Implementation of ASQM 1 at the ANAO
Including key changes to the ANAO’s quality management approach
- The Professional Services Group (PSG) was responsible for implementing ASQM 1. The PSG Group Executive Director has responsibilities for the maintenance of the ANAO Quality Management Framework, audit manual policies and methodologies.
- PSG developed a project plan and established governance arrangements for approvals of elements of the project.
- The ANAO established the quality objectives required by ASQM 1 and assessed our quality risks and identified our existing responses that addressed risks.
- We performed a gap analysis to identify whether there were any gaps in our responses to the risk or new requirements in ASQM 1, ASQM 2 and ASA 220.
- Where there were gaps, the ANAO designed additional responses to address the risks
- Quality objectives, risks and responses were reviewed by the ANAO Quality Committee
- Revisions to the ANAO Quality Management Framework (QMF) and ANAO Audit Manual were drafted by PSG
- The revisions were endorsed by the Quality Committee and then approved by the Auditor-General
- The QMF was published in July 2023 and the Audit Manual was published in August 2023.
- ANAO Internal Audit completed an internal audit over the planning of the ASQM 1 implementation project in 2022.
- ANAO Internal Audit completed an internal audit assessing the implementation of ASQM 1 in 2023.
- PSG communicated the changes arising from the new standards and system of quality management to all staff in training and regular communication.
- This included communication with individuals assigned ultimate and operations accountability and responsibility for the SOQM to ensure awareness of understanding of these obligations.
- Communications included email correspondence and town halls with the Auditor-General, bulletin notices on the ANAO intranet.
- The nature of these communications collectively reinforced the ‘tone at the top’ in relation to the expectations of uncompromising quality in delivering audit and other assurance engagements.
- They also provided information to management and business teams concerning what was changing, why the changes were important, and how the ANAO was responding.
Quality management framework
The ANAO Quality Management Framework is the ANAO’s system of quality management and is published on the ANAO website.

The elements of ASQM 1 are addressed in our Quality Management Framework.
Relevant ethical requirements
|
Quality objectives (ASQM 1 paragraph 29) |
|
The ANAO, its personnel and contract service providers understand, and fulfil their responsibilities in relation to the ethical requirements relevant to ANAO work. |
2.26 The ANAO Auditing Standards require the Auditor-General and ANAO staff to fulfill their responsibilities in accordance with relevant ethical requirements, including those pertaining to independence, which are set out in APES 110 Code of ethics for professional accountants (including independence standards) (APES 110).
2.27 The ethical requirements of APES 110 apply in addition to the ethical requirements that apply to ANAO staff as employees of the ANAO and as Commonwealth public servants. ANAO staff are bound by the ANAO Values and Behaviours, and the Australian Public Service (APS) Values and Code of Conduct set out in the Public Service Act 1999. ANAO staff are also bound by the General Duties of Officials under Part 2–2 Division 3 of the Public Governance, Performance and Accountability Act 2013.
The QMF sets out the ANAO quality objectives and the responses that address those objectives.
Audit policy and methodology impacts
The ANAO Audit Manual sets out the policies which auditors must comply with when undertaking audits.
The changes to the auditing standards have been integrated into the ANAO Audit Manual – Shared Content volume, which applies to all of our audit products.
The changes to the Manual were then integrated into our TeamMate audit methodology templates.
Areas of challenge
Implementation challenges
- ASQM 1 is extensive and covers elements that cover all areas of the ANAO including Corporate areas such as Human Resources management, Information Systems and Technology management as well as PSG and audit responsibilities.
- To undertake the initial gap analysis PSG needed to obtain an understanding of all the existing responses operating across the office, and determine whether there were gaps in the responses.
- The Quality Committee includes representatives from each area of the office, so allowed for collaboration across the ANAO at the senior level to ensure that responses were captured.
- Some practices weren’t explicitly documented.
- The ASQM 1 focus on culture and leadership commitment can be difficult to capture.
- There are many actions, decisions and messages that contribute to how culture demonstrates a commitment to audit quality – not necessarily tangible.
Evaluation of the quality management framework challenges
- ASQM 1 requires the annual evaluation of the design, implementation and operating effectiveness of the quality management framework.
- The challenges in gathering information to perform the gap analysis also arose in the evaluation.
- Information was required from across the office and some practices were not well documented to evidence that they were operating effectively.
- Availability of documentation – not all information was collated in one place.
- Assessing the operating effectiveness of the quality management framework requires judgement.
- Individuals may have different perspectives of how well the framework is operating.
- The evaluation requires an assessment of the severity and pervasiveness of deficiencies. This also requires judgement and people may have different views on severity.
Good practices, lessons learned and future work
Expansion of root cause analysis
The ANAO has been conducting root cause analysis (RCA) over quality assurance findings identified in financial statements audits for several years in anticipation of the implementation of ASQM 1.
In accordance with ASQM 1 the ANAO added a new policy requiring RCA to be conducted over quality assurance findings in all ANAO audit products.
2023 was the first year that RCA was conducted over quality assurance findings identified in performance audits.
Next year, the ANAO will expand the RCA program to quality assurance findings identified in performance statements audits.
Root causes analysis allows a deeper understanding of the drivers of quality deficiencies and assists in identifying the best remedial actions to address the deficiencies.
Information-gathering for evaluation

The ANAO will continue to make improvements to our processes to support the implementation and evaluation of the quality management framework.
More structured process of information-gathering, e.g., communicating requirements and timeframes to business areas.
Risk assessment
- The 2022-23 evaluation of the quality management framework informed the Quality Risk assessment for 2023-24.
- The quality risk assessment is used to identify if we have new risks, or areas where we need to design and implement new responses, or adjust existing responses.
- This reflects the ASQM 1 focus on iterative continuous improvement.